Effective PFAS Waste Management in Agricultural Environments
Effective PFAS Waste Management in Agricultural Environments
Blog Article
Your Overview to PFAS Treatment Technologies and Advantages
The prevalence of PFAS contamination in water sources demands a thorough understanding of readily available therapy innovations. Numerous techniques, such as triggered carbon purification, ion exchange systems, and advanced oxidation procedures, existing distinctive advantages in dealing with these persistent contaminants. Each innovation not just targets particular PFAS substances but additionally plays an essential role in boosting total water high quality and safeguarding environmental stability. As communities grapple with the implications of PFAS exposure, the option of an ideal therapy approach ends up being progressively vital, triggering a closer examination of these innovations and their respective benefits.
Understanding PFAS Contamination
Comprehending PFAS contamination is critical for addressing its pervasive impact on ecological and human wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) are a team of artificial chemicals widely used in various commercial and customer items because of their water- and grease-resistant buildings. Typically located in firefighting foams, non-stick pots and pans, and water-repellent textiles, PFAS have actually gone into the environment via manufacturing procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from land fills
Once launched, these substances continue in the environment, bring about prevalent contamination of dirt and water sources. Their unique chemical structure, identified by solid carbon-fluorine bonds, renders them immune to destruction, resulting in a sensation known as "forever chemicals." Subsequently, PFAS can accumulate in the body and the food chain, potentially creating unfavorable wellness effects, consisting of body immune system interruption, developing concerns, and an enhanced threat of certain cancers cells.
Governing companies and health companies are significantly recognizing the importance of PFAS contamination, triggering efforts to monitor, evaluate, and reduce its effects. Recognizing the pathways of PFAS contamination is crucial for notifying public plan and establishing effective strategies to shield both ecological and human health.
Introduction of Therapy Technologies
Different therapy modern technologies have been established to attend to the challenges presented by PFAS contamination in water and soil. These innovations can be generally categorized into several groups, each with its one-of-a-kind devices and efficiency in removing PFAS compounds.
One noticeable technique is ion exchange, which uses material products to capture and get rid of PFAS from polluted water. This approach is especially efficient for short-chain PFAS and can accomplish substantial decreases in focus degrees. One more innovation, progressed oxidation processes (AOPs), employs solid oxidants and ultraviolet light to damage down PFAS right into less hazardous compounds. AOPs appropriate for treating a large range of PFAS compounds yet may call for cautious optimization to take full advantage of effectiveness.

Activated Carbon Filtering
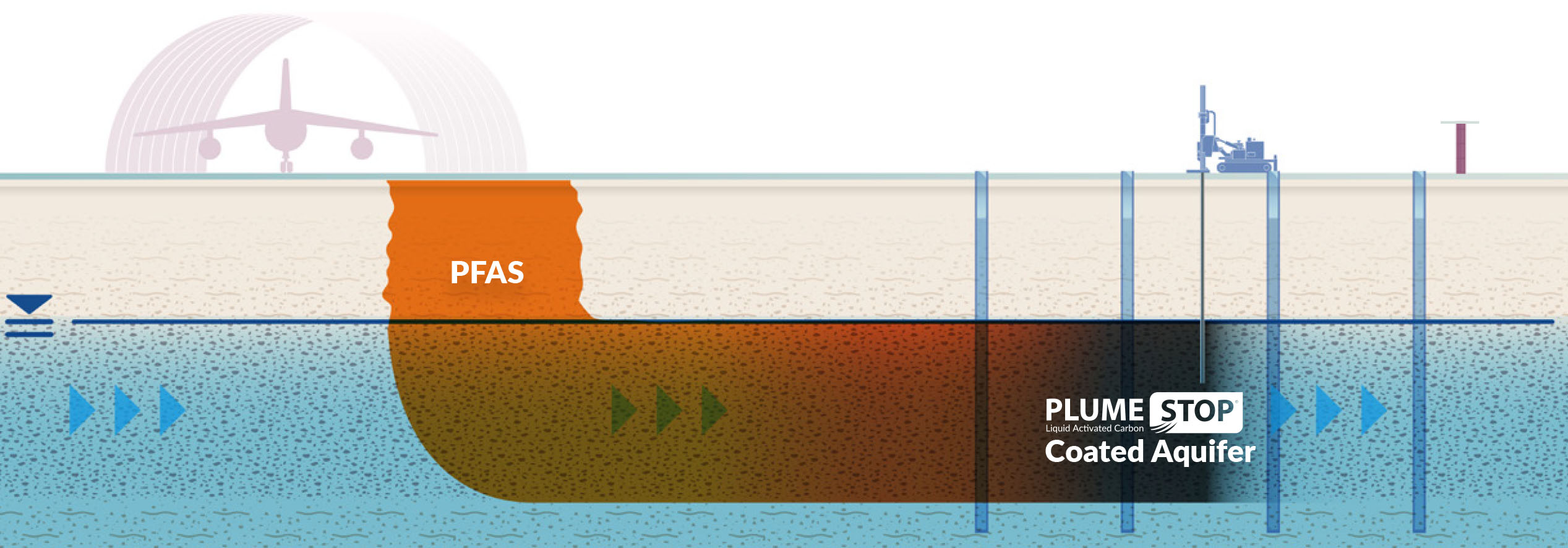
Turned on carbon filtering is an extensively used approach for the elimination of PFAS from infected water, known for its capacity to adsorb a wide variety of organic compounds. This technology employs turned on carbon, an extremely permeable material with a considerable area, which assists in the binding of PFAS particles via physical adsorption. The effectiveness of activated carbon in removing PFAS is influenced by a number of factors, consisting of the kind of carbon utilized, the call time, and the concentration of PFAS in the advice water.
Among the advantages of triggered carbon filtering is its flexibility; it can be applied in different arrangements, such as granular turned on carbon (GAC) systems or powdered triggered carbon (POLITICAL ACTION COMMITTEE) systems. GAC systems are typically employed in larger-scale applications, while PAC can be used in smaller sized or short-lived configurations. Moreover, the innovation is reasonably very easy to operate and maintain, making it available for several water treatment centers.
Ion Exchange Systems
Ion exchange systems stand for another efficient strategy for the removal of PFAS from infected water, matching methods like activated carbon purification. These systems operate the concept of exchanging ions in the water with ions held on a resin product. Ion exchange resins can be particularly developed to target the adversely charged PFAS compounds, successfully catching them and allowing cleaner water to pass through.
Among the key benefits of ion exchange other systems is their ability to eliminate a variety of PFAS, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain versions. This versatility makes them suitable for numerous applications, varying from community water treatment to commercial procedures. Furthermore, ion exchange systems can often attain lower detection limitations for PFAS contrasted to some various other therapy methods, thus enhancing water quality.
However, it is vital to keep an eye on and take care of the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the efficiency can decline over time due to saturation. Correct upkeep and substitute of the material are crucial for sustaining the system's efficiency. On the whole, ion exchange systems offer a reliable and efficient solution for PFAS elimination, contributing considerably to risk-free alcohol consumption water criteria and environmental management.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) use powerful oxidants to effectively break down PFAS compounds in infected water. These innovative treatment methods generate highly responsive types, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down complicated PFAS molecules right into less hazardous byproducts. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs commonly use combinations of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, boosting the oxidation potential and improving degradation effectiveness
The primary advantage of AOPs hinges on their capacity to target a wide variety of PFAS compounds, including both long-chain and short-chain versions. This flexibility is crucial, as PFAS contamination often entails blends of different substances with differing chemical structures. Additionally, AOPs can be integrated right into existing water therapy systems, making them a sensible view website option for lots of communities and markets.
Nevertheless, the implementation of AOPs can be resource-intensive, requiring cautious consideration of functional expenses and energy consumption. In addition, while AOPs are effective in breaking down PFAS, they may not entirely eliminate all byproducts, requiring further therapy steps - m270 pfas treatment. In general, AOPs represent an encouraging avenue for resolving PFAS contamination, contributing to cleaner water sources and boosted public wellness protection

Verdict
By selecting the appropriate innovation, communities can enhance water quality, protect public health and wellness, and mitigate the environmental threats associated with PFAS exposure. Continued study and implementation of these methods are essential for effective management of PFAS contamination in influenced locations.
Report this page